SPOOF AND PHISHING EMAIL ADVISORY
SPOOF AND PHISHING EMAIL ADVISORY
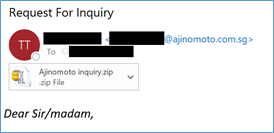
We have recently been alerted to an instance of an email that was sent to a member of the public, impersonating us and our employee. The email appears to have been sent from a generic email address ending with “@ajinomoto.com.sg”, and contains a zip folder attachment (.zip). The body of the message suggests that you open the attachment to review a quotation, and asks that you respond to the email urgently with instructions and the payment method.
Please understand that this email was a spoof email and was not sent by Ajinomoto Singapore. We have lodged a police report in respect of this incident.
Email spoofing is a technique used in spam and phishing attacks to trick recipients into thinking a message came from a person or entity they either know or can trust. In spoofing attacks, the sender forges email headers so that the recipient’s email software displays the fraudulent sender address, which most recipients believe. Unless they inspect the header more closely, recipients see the forged sender in a message. As a result, recipients will click malicious links, or open attachments that contain malware.
Please be alert if you receive an email that appears to have been sent by us, inviting you to open email attachments or click on links contained in the email. This is especially if you do not expect to hear from us. Phishing or spoof emails may be in various forms. When in doubt, please do not open any email attachments, or click on any links that may be contained in the email that you receive from us.
Here are a few useful tips to help you ascertain the genuineness of an email:
(a) Never click links in a suspicious email or email that you do not expect. If you are unsure, always type the official domain in your browser and authenticate directly on the site.
(b) Please check your email header to ensure that the sender’s domain is genuine and correct before you reply.
(c) Copy and paste the content of an email message into a search engine. The chances are that text of the email may be used in a common phishing attack has already been reported and published.
(d) Be suspicious of email supposedly from an official source with bad spelling or grammar.
(e) Avoid opening attachments from suspicious or unknown senders.
(f) Beware of emails that create a sense of urgency or danger. Phishing or spoof emails often try to create a sense of urgency to respond.
(g) Do not provide any personal, financial or other sensitive information, such as your bank account details.
Below is an example of an email that appears to be from Ajinomoto Singapore (i.e. a forged email), but which Ajinomoto Singapore did not send and also XXX@gmx.com is not our email domain/address (as can be seen from the internet header and the “Reply-to” path):

You may also visit the National Crime Prevention Council’s scamalert.sg website for more information about various types of scams.
Ajinomoto (Singapore) Pte. Ltd.
